Bitdefender informed Google of validated attack methods, but the tech giant won’t address them, citing misalignment with its threat model and confidence in existing security measures.
Bitdefender Labs, a Native XDR platform, has released its findings on novel attack techniques exploiting Google Workspace (formerly G Suite). According to Bitdefender’s technical report authored by Martin Zugec, threat actors can escalate a single compromised machine into a network-wide breach using previously unknown methods, leading to the deployment of ransomware or data exfiltration.
Researchers found the issues when developing their XDR sensor for Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and Google Workspace. The report, published on 15 November 2023 and shared with Hackread.com ahead of publication, highlights different pathways to achieve this escalation.
Researchers noted that from a single compromised machine, attackers could move laterally to multiple cloned machines with Google Credential Provider for Windows (GCPW) installed, evade multi-factor authentication mechanisms, and access the cloud platform with custom permissions. They can even decrypt locally stored credentials used to recover passwords to expand their attack scope beyond the Google platform.
For your information, GCPW enables remote Windows device management features without requiring a VPN connection or domain registration. It allows SSO (single-sign-on) authentication to Windows OS with Google Workspace credentials.
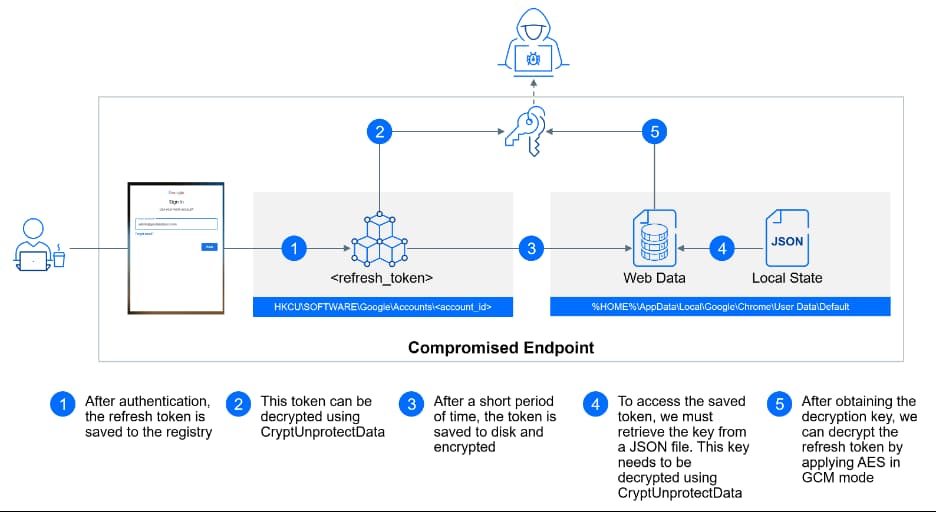
The GCPW uses a local ‘Gaia’ service account to authenticate users with Google Workspace credentials. This account is created when GCPW is getting installed and has escalated privileges.
The feature integrates a Credential Provider into the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) that performs authentication in Windows OS. This Credential Provider verifies user credentials when they unlock or log into their devices.
When a new user authenticates with GCPW, the created ‘Gaia’ account creates a new local user account for them, which is linked with their Workspace account. The user logs in using this local profile, and a refresh token is stored in their profile to prevent multiple authentication prompts.
Let’s examine the attack methods Bitdefender researchers have identified in their blog post.
Method 1: Moving to other cloned machines with GCPW installed
It is worth noting that the ‘Gaia’ account is created with a random password, and therefore, despite existing on all machines, each will have a unique password for ‘Gaia.’ But if a machine is created by cloning another one on which GCPW is already installed, the password would also get cloned. So, if one knows the password of a local account and all local accounts linked with the devices share the same password, one will know passwords to all these devices.
Method 2: Gaining access to the cloud platform with custom permissions
An adversary can exploit a vulnerability in GCPW to access the GCP with custom permissions by using the ‘Gaia’ service account and creating a service account key with custom permissions. They can use the key to authenticate with GCP.
Method 3: Decrypting locally stored passwords
Attackers can use the ‘Gaia’ service account to decrypt locally stored passwords using the account’s access to the Windows Credential Manager. They can use the stored credentials to authenticate with other services or applications.
These attack methods allow escalation of compromise from a single endpoint to an entire network.
Bitdefender notified Google, and the search engine giant confirmed that their discovered attack methods were valid. However, the company does not intend to address them at the moment because they do not fall into its predetermined threat model, and security measures should be enough to counter them.
Bitdefender has included detections for the attacks in GravityZone XDR to help the security community address them.
RELATED ARTICLES
- Google Account Sync Vulnerability Exploited to Steal $15M
- Google Indexed Trove of Bard AI User Chats in Search Results
- Hive Ransomware is now as Hunters International, Bitdefender
- Phishers Exploiting Google Docs to Harvest Crypto Credentials
- Fantom Foundation Suffers Wallet Hack Via Google Chrome Flaw