Another day, another malware aiming at Windows devices – This time, the malware is spread from YouTube.
The IT security researchers at Russian anti-virus vendor Dr. Web have discovered a dangerous malware campaign being spread by cybercriminals from YouTube, a popular video-sharing website owned by Google.
Dubbed Trojan.PWS.Stealer.23012 by researchers, the malware is written in Python programming language and aims at targeting Microsoft Windows-based devices, steals login credentials for emails and social media accounts.
According to a blog post by Dr. Web, cybercriminals are posting malicious links in the comments and video description sections of YouTube videos, especially those videos which are based on gaming hacks and cheats using special applications.
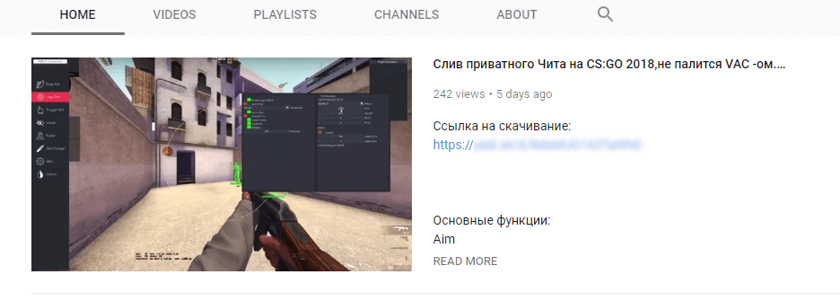
The cybercriminals lure users into clicking on the link which would supposedly allow them to access gaming cheats and other useful utilities. But, in reality, these links take users to Yandex Disk servers, a Russian cloud service offered by Yandex, allowing users to store files on “cloud” servers and share them with others online.
Once there, the victim can see several videos containing user comments stating that the file they are about to download is clean and legitimate. However, Dr. Web noticed that all the comments on those videos are fake and posted by cybercriminals using fake profiles.
In case the victim is tricked into clicking the link it downloads a self-unpacking RAR archive file containing Trojan.PWS.Stealer.23012. Upon installing the file, it infects Windows computer and steals cookies from web browsers including Chrome, Opera, Vivaldi, and others.
Furthermore, the malware steals login credentials saved in victim’s web browser and take screenshots of user’s activity on their device. Moreover, it copies files from Windows Desktop. In this case the targeted file extensions include “.txt”, “.pdf”, “.jpg”, “.png”, “.xls”, “.doc”, “.docx”, “.sqlite”, “.db”, “.sqlite3”, “.bak”, “.sql”, and “.xml.”
After gathering the data, the malware stores it on the device’s folder “C:/PG148892HQ8” on C drive in Spam.zip folder and send it to the command and control servers (C&C) set up by the cybercriminals along with the victim’s location.
Dr. Web researchers have also identified a modified version of this malware dubbed Trojan.PWS.Stealer.23198. Therefore, gamers and YouTubers are advised to avoid clicking on links users left in the comment section of Youtube or any other site until they are verified by the site administrator/moderator.
Remember this is not the first time when YouTube has been used for malicious purposes. In January this year, hackers used YouTube to infect users’ computers with cryptojacking malware that used their device’s computing power to mine Monero cryptocurrency.
Also, gaming mods and cheat files are nothing new to malware infection. There have been several incidents involving Grand Theft Auto (GTA) IV, GTA V, Steam, Call of Duty, Assassin’s Creed and Minecraft where hackers were found spreading infected mods on the Internet.
