The new variant of Agent Tesla is equipped with many sophisticated features, including credential-stealing modules.
According to senior threat researcher at SentinelOne, Jim Walter, a new variant of Agent Tesla malware has surfaced. It is equipped with credential-stealing modules and can steal passwords from email clients, VPN software, web browsers, Wi-Fi networks, and FTP apart from many popular apps.
The new variant is specifically programmed to steal login credentials from Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Edge, OpenVPN, and browsers, including Chrome, Safari, Opera, Mozilla Thunderbird, and Firefox.
Agent Tesla is a RAT/remote access trojan, which researchers believe is among the most predominant malware families that threatened enterprises early on in 2020. It was used even more than Emotet, Dridex, and TrickBot malware.
Agent Tesla was firstly discovered in 2014, and the malware underwent steady growth in the past two years. Initially, Agent Tesla was sold on commonly used hacker forums and marketplaces.
The malware developers sold it through the now-defunct website AgentTesla (dot) com, from where it was directly sold to individual customers and management panels to let them quickly sort the collected data. Despite being over six years old, the malware’s continuous evolution is a cause of concern for security researchers.

During the COVID-19 pandemic, the malware was embedded with new functionalities and widely used in coronavirus-themed scams and phishing campaigns. The information that the malware collects from infected devices is quickly transferred to the attacker through the panel interface.
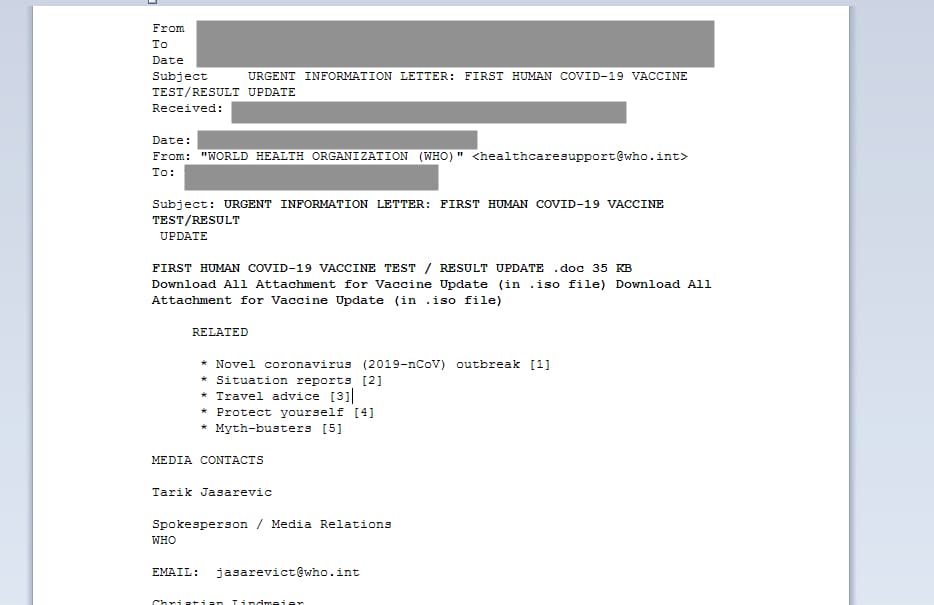
After harvesting the app configuration data and credentials from a targeted app/program, the malware delivers it to a C&C server through STMP or FTP using the internal configuration credentials.
“Attackers are continually evolving and finding new ways to use tools like Agent Tesla successfully while evading detection,” researchers warned. “When combined with timely social engineering lures, these non-sophisticated attacks continue to be successful. Detection and prevention are key to reducing exposure to these threats,” researchers advised.
Luckily, Agent Tesla isn’t as sophisticated as it is believed to be. Its primary mode of distribution is phishing scams, and recently it is identified in coronavirus-themes attacks, especially campaigns that involve the distribution of emails from the WHO.
It is also intelligently embedded in specially designed Office documents. So, informed use of the internet is your best defense against Agent Tesla. For instance, you should avoid clicking on suspicious emails, specifically those containing unexpected attachments.
Did you enjoy reading this article? Do like our page on Facebook and follow us on Twitter.
