Adrozek malware was identified by Microsoft and since May 2020 over 30,000 users have been infected.
With companies helping each other find vulnerabilities and patch them, the job for malicious hackers gets much more difficult. In the latest, Microsoft has discovered a malware campaign that has infected over 30,000 users since May 2020 with the Adrozek malware.
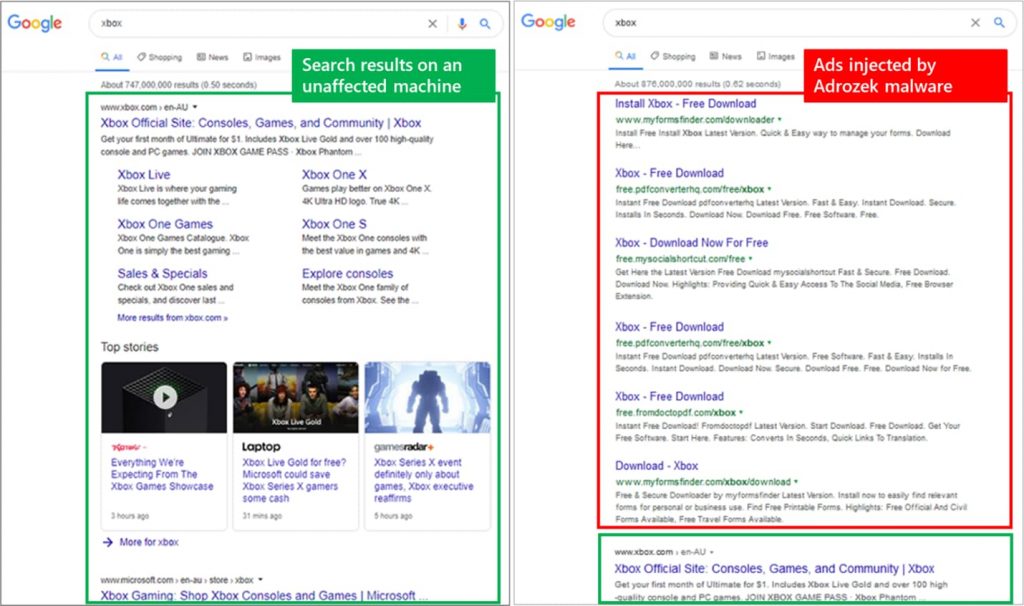
It has been found to be spreading globally and targets web browsers such as Microsoft Edge, Google, Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Yandex which are being run on Windows in order to “inject ads into search results.”
See: New Agent Tesla variant steals passwords from web browsers & VPNs
The purpose of these ads is to prompt users to click on them which would redirect them to affiliated sites and therefore end up making money for the malware developers.
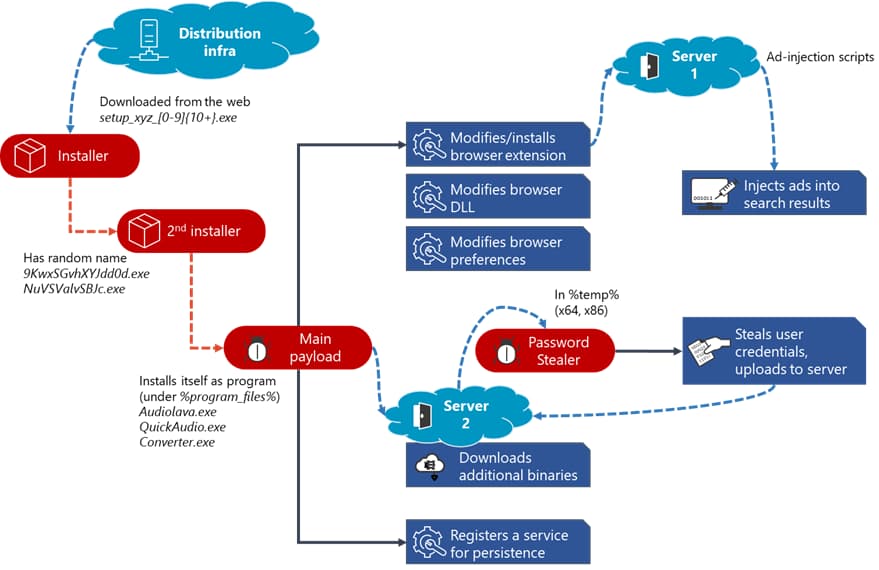
How the Adrozek malware initially infects users is by putting an executable file into the “Temp” folder found in Windows. This file which poses as audio software but in reality is malicious then downloads the infectious file which is responsible for making the malware run.
Once run, it adds new browser extensions, changes the in-browser DLL files, and changes the browser’s settings including the default homepage, default search engine, updates schedule, permissions settings, and much more in order to do its job of inserting malicious ads.
Explaining further, Microsoft states in a blog post that,
In our tracking of the Adrozek campaign from May to September 2020, we saw 159 unique domains used to distribute hundreds of thousands of unique malware samples. Attackers relied heavily on polymorphism, which allows attackers to churn huge volumes of samples as well as to evade detection.
While many of the domains hosted tens of thousands of URLs, a few had more than 100,000 unique URLs, with one hosting almost 250,000. This massive infrastructure reflects how determined the attackers are to keep this campaign operational.
But this is not all. In Mozilla Firefox, the Adrozek malware also steals user credentials which are communicated back to the attackers making it more complicated than it seems on the surface with its main ad injection feature.
See: Flaw in Safari browser’s API implementation lets user files to be stolen
To conclude, according to the tech giant, modifying browsers is not a new attack vector and has been experienced before. However, being able to modify several browsers together makes it more alarming.
If you believe you may have been infected, you should re-install all browsers on your system regardless of if you use them and also install reputable anti-virus software in order to automatically guard against such threats.
Did you enjoy reading this article? Don’t forget to like our page on Facebook and follow us on Twitter!

Thanks for this information
Thnx for the post. I found it very helpful for me because I had just learned these things.